How To Add Physics In Blender
Collision
Reference
- Style
-
Object Way
- Console
Particles, Soft Bodies and Cloth objects may collide with mesh objects. Boids effort to avoid Collision objects.
-
You may limit the consequence on particles to a group of objects (in the Field Weights panel).
-
Deflection for soft body objects is difficult, they ofttimes penetrate the colliding objects.
-
Hair particles ignore deflecting objects (merely you lot tin can breathing them as soft bodies which have deflection into account).
If you change the deflection settings for an object you have to recalculate the particle, soft trunk or cloth organization by Delete Bake, this is not done automatically.

A collider object can exist temporarily disabled via an animatable toggle to the right of the button that permanently activates or deactivates information technology.
Options
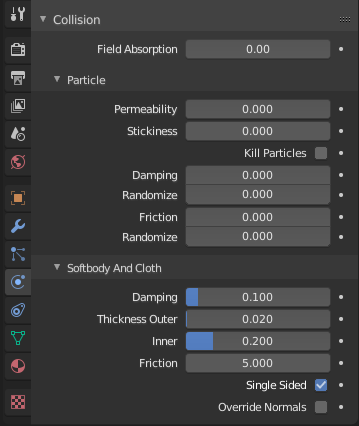
Collision panel.
Standoff
- Field Absorption
-
A deflector tin also deflect effectors. You tin can specify some collision/deflector objects which deflect a specific portion of the effector force using the Field Absorption value. 100% absorption results in no force getting through the collision/deflector object at all. If you have iii standoff object behind each other with eastward.g. 10%, 43% and three%, the absorption ends upwards at effectually 50% \(100 × (1 - 0.1) × (1 - 0.43) × (1 - 0.03)\).
Particle
- Permeability
-
Fraction of particles passing through the mesh.
- Stickiness
-
How much particles stick to the object.
- Kill Particles
-
Deletes Particles upon impact.
- Damping
-
Damping during a collision (independent of the velocity of the particles).
- Randomize
-
Random variation of damping.
- Friction
-
Friction during movements along the surface.
- Randomize
-
Random variation of friction.
Soft Trunk and Textile
Information technology is besides important to note that this collision panel is used to tell all simulations that this object is to participate in colliding/deflecting other objects on a shared layer (particles, soft bodies, and cloth).
Note
The object's shape deforms the cloth, so the material simulation must be inputted the "true" shape of that mesh object at that frame. This true shape is the basis shape as modified past shape keys or armatures. Therefore, the Standoff Modifier must be subsequently whatever of those. The image to the right shows the Modifiers panel for the Character mesh object (non the cloth object).
- Damping
-
Damping during a collision. The amount of bounce that the surfaces will have.
-
0.0 - No damping, soft bodies volition have a maximum bounce.
-
i.0 - Maximum damping, soft bodies will not bounce at all.
-
- Thickness
-
A padding distance is added to the inside and outside of each face up, to help to prevent intersections. The soft body volition come to residue at this distance away from the face of the colliding object. Outside and inside is defined by the face up normal, depicted as blue pointer in Fig. A soft body vertex colliding with a plane..
- Outer
-
Size of the outer collision zone.
- Inner
-
Size of the inner collision zone (padding distance).
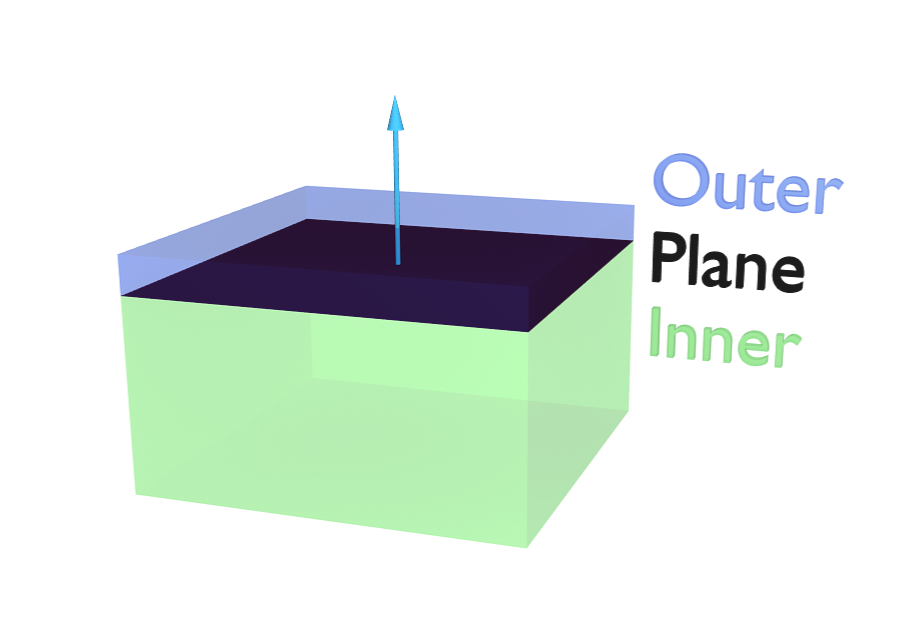
A soft torso vertex colliding with a plane.
- Friction
-
A coefficient for how slippery the cloth is when information technology collides with itself. For instance, silk has a lower coefficient of friction than cotton.
- Single Sided
-
When enabled, the collider is considered to correspond the boundary of a solid object rather than a sparse surface, and ejects intersecting cloth in the direction of its normal.
- Override Normals
-
When enabled, cloth collision impulses human activity in the management of the collider normals.
Note
Soft body collisions are difficult to go perfect. If one of the objects move too fast, the soft body will penetrate the mesh. Encounter also the section about Soft Bodies.
Examples

Deflected particles.
Here is a Meta object, using Instancing Vertices to a particle system emitting downward, and deflected past a mesh cube.
Hints
-
Make sure that the normals of the mesh surface are facing towards the particles/points for correct deflection. Negative scales on the object can accept a similar effect. Brand sure to recalculate the normals after applying the scale.
-
Hair particles react directly to force fields, and so if you lot use a forcefulness field with a brusk range you do not need necessarily collision.
-
Hair particles avert their emitting mesh if yous edit them in Particle Edit Mode. So you can at least model the pilus with collision.
How To Add Physics In Blender,
Source: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/physics/collision.html
Posted by: halcombpuffined.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Add Physics In Blender"
Post a Comment